Single-Action Stainless Steel Cylinders for
Scissor Lift Tables up to 160 bar // HZE4-VA
General Information
The HZE4-VA series was specially developed for installation in lifting tables up to 160 bar. It is characterized by a robust design with minimal installation dimensions. The cylinders are designed in accordance with EN1570 (lifting platforms) up to an operating pressure of 160 bar. The cylinders are supported by maintenance-free spherical plain bearings. The connection bore is designed for a pipe rupture safety device or for a lowering brake valve. Depending on the installation position, the cylinder can be vented via the vent screw on the rod side. Depending on the application, the cylinders are supplied with different seal sets. Different piston rod materials are available.
Length and stroke tolerances according to DIN7168g (see >>Technical Information)
Technical Information | |
|---|---|
| Maximal operating pressure | = 160 bar |
| Testing pressure | = 210 bar |
| Rod Ø | = 40 – 100 mm |
| Accepted temperature range of the hydraulic fluid | = -20°C up to +80°C |
| Hydraulic fluid | = mineral oil (HL, HLP) according to DIN 51524 & DIN 51525 (standard) |
| Stroke speed | = ≤ 0,5 m/s |
Mounting Types | |
|---|---|
| Ball-and-socket joint on both sides | (UK- Standard) |
| (UK- Standard) |
Additional Information
Connecting Bore
The connection hole is located at the bottom end of the cylinder and is designed for line break valves.
The position on the circumference can be changed (standard P8).
Drawing of the position of the vents P7 and the connection piece P8
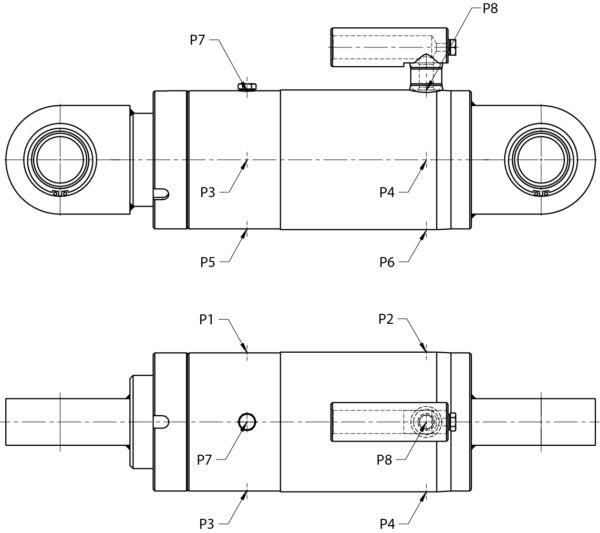
For long strokes, the support width of the piston rod in the cylinder tube can be changed in order to reduce the load on the guide system when fully extended. This also depends on the type of installation and the design of the cylinder.

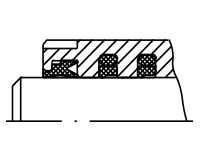
D1 - Groove ring and scraper made of polyurethan (standard) | |
|---|---|
| Temperature range | -30°C to +80°C |
| Hydraulic fluid | Mineral oil |
| Stroke speed | ≤ 0,5 m/s |
| Application | Standard seal set for normal operating conditions, offers very high resistance to wear |
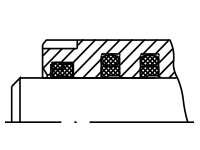
D2 - Axial seal ring set consisting of PTFE STEP SEALS (O-ring seal made of NBR) - double scraper (polyurethane) | |
|---|---|
| Temperature range | -30°C to +100°C |
| Hydraulic fluid | Mineral oil, flame-retardant hydraulic fluids HFA and HFB up to +40°C; HFC up to +60°C |
| Stroke speed | ≤ 1 m/s |
| Application | Seal set for high sliding speeds, no stick-slip effect, higher leakage compared to D1 and D3 |
D2V - Axial seal ring set consisting of PTFE STEP SEALS (O-ring seal made of Viton)Double scraper (Viton O-ring seals) | |
|---|---|
| Application | Sealing set for high sliding speeds, no stick-slip effect, greater leakage than in the case of D1 and D3, for higher temperatures (+200°C) and fluids on a phosphate ester basis (HFD) |

D3 - Tandem sealing set consisting of groove ring (polyurethane) and PTFE STEP SEAL | |
|---|---|
| Temperature range | -30°C to +80°C |
| Hydraulic fluid | Mineral oil |
| Stroke speed | ≤ 0,8 m/s |
| Application | Sealing set for high loads at minimum leakage, smooth-running stroke movements |
Theoretical cylinder force in [kN] (efficiency = 100%)
Rod Ø [mm] | Piston Area [mm²] | Operating Pressure [bar] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 160 | |||
| 40 | 1256,6 | 6,3 | 12,6 | 20,1 | |
| 50 | 1963,5 | 9,8 | 19,6 | 31,4 | |
| 60 | 2827,4 | 14,1 | 28,3 | 45,2 | |
| 70 | 3848,5 | 19,2 | 38,5 | 61,6 | |
| 80 | 5026,5 | 25,1 | 50,3 | 80,4 | |
| 90 | 6361,7 | 31,8 | 63,6 | 101,8 | |
| 100 | 7854,0 | 39,3 | 78,5 | 125,7 | |
Knickung
Grundlagen siehe >>Technische Grundlagen
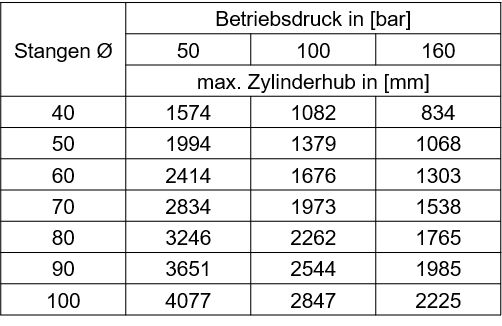
Tabelle: zulässige Hübe (im elastischen Bereich) in mm // Knicksicherheit Sk=3,5