Force and Movement Ratios of a Double-Action Cylinder
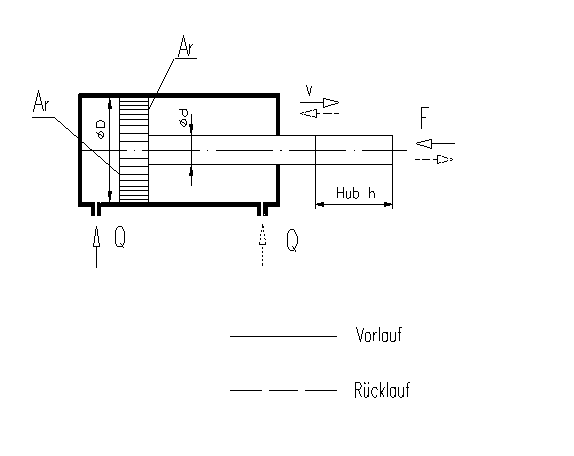
If an external force F acts on a piston, this force creates a pressure on the piston area Ak. Conversely, this force is also a resistance that the pump delivery Q meets. In this way, a pressure builds that acts evenly on all sides, including the piston area Ak. The piston can thus now exert a force itself according to the following formula:
F = p * Ak
F = p * Ar (analogously for the return)
| F | = | Piston Force | in [N] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ak | = | Piston area |
(D² *3,14) 4 |
in [mm²] |
| Ar | = | Piston ring area |
(D²-d²) * 3,14 4 |
in [mm²] |
| D | = | Piston diameter | in [mm] | |
| d | = | Rod diameter | in [mm] | |
| h | = | Travel length | in [mm] | |
| Q | = | Feed flow | in [l/min] | |
| t | = | Travel time | in [s] | |
| v | = | Travel speed | in [m/s] |
Contact
- Strautmann Hydraulik GmbH & Co. KG
-
Gausekamp 15
49326 Melle-Wellingholzhausen - 05429 9404-0
- info@strautmann-hydraulik.de
- bewerbung@strautmann-hydraulik.de
